State of Natural Resources interim report 2019: Challenges

Climate and biodiversity: two interconnected challenges
The nature and climate emergencies are interlinked.
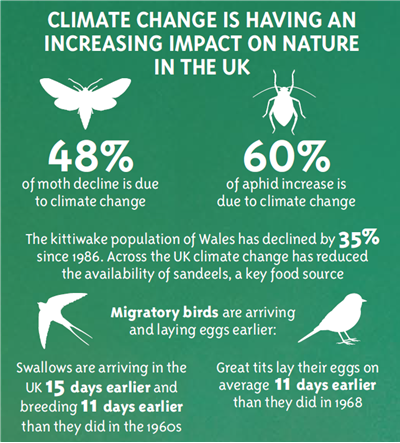
Climate change is driving species to move location.
Arctic-alpine species within mountain habitats could disappear from Wales as their habitats are lost.
Where coastal plants and wildlife cannot move inland, sea-level rise and increased land erosion could lead to widespread loss.
The ecosystem services these habitats provide - like flood defence and carbon dioxide removal - will also be lost.
The number and range of invasive non-native species is likely to increase with the changing climate.
Climate emergency
Global assessments
Global greenhouse gas emissions are at levels unprecedented in at least the last 800,000 years.
The Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change warned that the world must reach global net-zero greenhouse gas emissions by 2050 to avoid the consequences of warming above 1.5 degrees C.
Staying within these limits - which is still possible - will reduce risks to biodiversity, ecosystems, food systems, water and human wellbeing.
When the report was published it led to a change in public perception of climate change.
There is now an urgent need for a response across government and society.
Wales' greenhouse gas emissions
Greenhouse gas emissions in Wales have fallen by a quarter since 1990.
This is mainly due to more efficient energy generation, natural gas replacing coal, chemical industry decline, waste reduction and changes in manufacturing output.
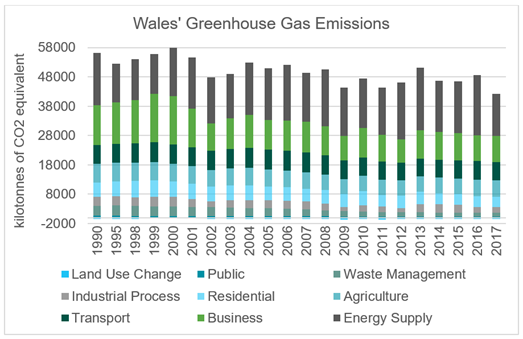
Source: National Atmospheric Emissions Inventory
The third annual Well-being of Wales (2019) report gives more detail about the two sectors in Wales emitting the largest amount of greenhouse gases: energy and transport.
Read more about the energy and transport sectors in Wales.
Wales' targets for greenhouse gas emissions
In 2019, Welsh Government accepted the UK Committee on Climate Change recommendation that Wales should achieve 95% emission reduction by 2050.
This is greater than the Environment (Wales) Act 2016 requirement to reduce carbon emissions by at least 80% by 2050.
Welsh Government's priority is to reduce emissions from fossil fuel power generation.
The equivalent of 50% of Wales' electricity consumption was met from renewable sources in 2018. By 2030, the aim is to generate enough electricity from renewable sources to meet 70% of Wales’ electricity needs.
As well as having at least a gigawatt of Welsh-owned generation by 2030, all new energy developments should have some local ownership from 2020.
Prosperity for All: A Low Carbon Wales sets out the Welsh Government plan for meeting decarbonisation targets in Wales.
UK greenhouse gas emission targets
Following the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change report, the UK Committee on Climate Change reviewed the UK's decarbonisation targets.
It proposed a change to the UK target for greenhouse gases from an 80% reduction by 2050 to net zero emissions by 2050.
To deliver this revised target, it said:
- Almost all heating of buildings must be low carbon.
- A fifth of UK agricultural land must shift to uses which support emissions reduction, such as tree planting, biomass production and peatland restoration.
- We need a 20% reduction in the consumption of lamb, beef and dairy.
- Industrial resource efficiency must improve, with longer lasting products using less resources, alongside increased reuse and recycling.
- Supply of low carbon electricity must quadruple.
Nature emergency
Environmental pressures are causing global biodiversity declines at rates not previously encountered in human history.
The rate of species extinctions is accelerating.
Nature plays an essential role in providing food, energy, medicines and genetic resources.
If changes aren't made now, losses of biodiversity and the negative impact on nature’s benefits to people will continue.
Global assessments
In 2019, the International Science-Policy Platform on Biodiversity and Ecosystem Services published a global assessment of biodiversity.
It estimated that around 1 million animal and plant species across the world are now threatened with extinction.
The 2018 Living Planet Index is a global measure of the health of 16,704 populations of 4,005 species. It shows a 60% decline between 1970 and 2014.
UK assessments
The UK picture is reflected in the 2019 State of Nature report.
It shows how human impacts are driving changes in wildlife across the UK:
- Of the 8,431 species in the UK assessed by the IUCN Regional Red List, almost 1 in 7 are at risk of being completely lost.
- Thirty-two plants, 33 fungi and lichens, seven vertebrates and 61 invertebrates are known to have gone extinct over the last 500 years.
- Since 1970, the abundance of priority species has declined by 60% and their distribution has declined by just over a quarter. Declines in farmland birds have been more severe than those for any other habitat, with a decline of 54% in the Farmland Bird Indicator since 1970.
In Great Britain, 6% of non-native species are considered to be having a negative impact on biodiversity.
Over the period 1960 to 2018, invasive non-native species have become more prevalent.
This has increased the pressure on native biodiversity, outlined in detail in the UK Biodiversity Indicators 2019.
Every six years the UK's Joint Nature Conservation Committee assesses the conservation status of all species and habitats listed in Article 17 of the Habitats Directive.
The fourth Article 17 UK Habitats Directive Report (2019) found that 35% of listed species and 8% of habitats were in favourable conservation status at the UK level:
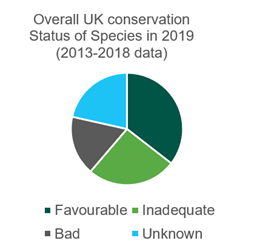
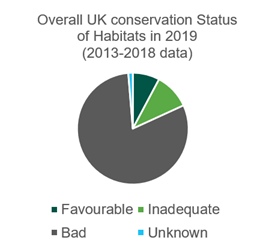
Source: Joint Nature Conservation Committee
Biodiversity in Wales
The 2019 State of Nature report found that 1 in 6 species are at risk of extinction.
Since rigorous scientific monitoring began in the 1970s, of the 3,902 species assessed in Wales, 73 have been lost.
Birds like turtle doves and corn buntings are now lost from Wales.
For the land-based and freshwater species in the UK assessments found in Wales, 10% of plants, 8% of fungi and lichens, 36% of vertebrates and 5% invertebrates are at risk of extinction.
Risk assessments of species extinction for Wales only are limited, as is an assessment of abundance. The State of Nature 2019 report shows us that there have been big changes in where wildlife is found across Wales:

Source: State of Nature Report 2019
Key factors affecting biodiversity
Key pressures affecting biodiversity loss across the UK and Wales result from:
- agricultural management
- climate change
- urbanisation
- pollution
- hydrological change
- invasive non-native species
- woodland management
Source: State of Nature Report 2019
Read more about the drivers of change in the International Science-Policy Platform on Biodiversity and Ecosystem Services global assessment (2019) and State of Nature report (2019).
Biodiversity loss and well-being
The pressure of climate change and loss of biodiversity affects the services ecosystems provide to us and, as a result, our well-being.
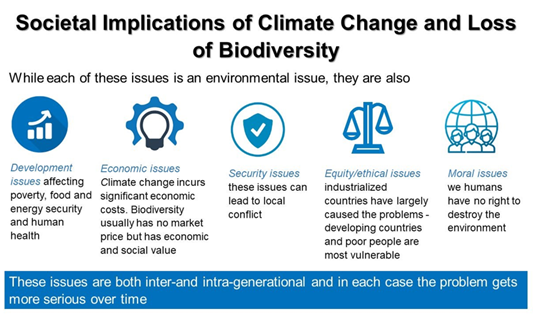
Source: 2019 IPBES report Global Assessment Report on Biodiversity and Ecosystem Services
Room for hope
As the State of Nature report says, the figures are mainly cause for alarm, but there is room for cautious hope.
Woodland cover has almost quadrupled across Wales, from 4% in the early 1900s to 15% today.
Polecats are also making a slow recovery from a low point in the 1930s.
The report also highlights conservation initiatives aiming to help nature restoration - the Celtic Rainforests Wales EU LIFE project, for example, aims to protect and enhance the ancient Western Atlantic Oakwoods of Wales.
The report goes on to recognise how conservation organisations and individuals have saved various species from extinction. The bittern and the large blue butterfly are two examples brought back from the brink of extinction in the UK.
Responding to the challenges
Find out how we can respond to the challenges of climate change and biodiversity loss.




